| AppleOrAndroid | College |
|---|---|
| Apple | Business |
| Apple | CFAC |
| Apple | Business |
| Apple | CMS |
| Apple | Engineering |
Comparing Multiple Proportions
Research Objective
Research Question: Is there a relationship between which college someone is in and whether they use an apple or android phone?
Population: All BYU students.
Parameter of Interest:
- We have a lot! We want to know the proportion of students in each college/phone combination. For example, \(\pi_{\text{Apple,Humanities}}\).
Sample: A convenience sample of 1727 BYU students who are in my class and completed the student survey.
Are there any issues with this study setup?
More Problem Definitions
Response Variable (y):
- Does the student have an Apple or Android phone. This is a categorical variable meaning it has to be one of a certain number of categories.
Explanatory Variable (x):
- The college.
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Main goal: Examine the RELATIONSHIP between College and Phone.
EDA Tool #1 - Grouped Bar Charts

EDA Tool #2 - Grouped Bar Charts Proportions

EDA Tool #3 - Tables of Counts
| Apple | Android | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business | 557 | 51 | 608 |
| CFAC | 119 | 19 | 138 |
| CMS | 140 | 37 | 177 |
| Education | 95 | 16 | 111 |
| Engineering | 84 | 19 | 103 |
| FHSS | 91 | 16 | 107 |
| Humanities | 23 | 8 | 31 |
| Life | 329 | 39 | 368 |
| Nursing | 77 | 7 | 84 |
| Sum | 1515 | 212 | 1727 |
EDA Tool #4 - Conditional and Marginal Distributions
Main Idea: Convert counts to proportions to account for differences in count sizes
Conditional Distribution of Row Variable given Column Variable:
- proportions sum to 1 down the rows
- divide cell counts by column totals
Conditional Distribution of Column Variable given Row Variable:
- proportions sum to 1 across the columns
- divide cell counts by row totals
EDA Tool #4 - Conditional and Marginal Distributions
Marginal Distribution of Column (or Row)
- proportions sum to 1 across total column (or row)
- divide column (or row) totals by table total
Relationship between variables is probably present if conditionals are different than marginal distributions.
Cond. Dists of Col. Given Row
| Apple | Android | |
|---|---|---|
| Business | 0.916 | 0.084 |
| CFAC | 0.862 | 0.138 |
| CMS | 0.791 | 0.209 |
| Education | 0.856 | 0.144 |
| Engineering | 0.816 | 0.184 |
| FHSS | 0.850 | 0.150 |
| Humanities | 0.742 | 0.258 |
| Life | 0.894 | 0.106 |
| Nursing | 0.917 | 0.083 |
| Margin (Overall) | 0.877 | 0.123 |
Cond. Dists of Row Given Col.
| Apple | Android | Margin (Overall) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business | 0.368 | 0.241 | 0.352 |
| CFAC | 0.079 | 0.090 | 0.080 |
| CMS | 0.092 | 0.175 | 0.102 |
| Education | 0.063 | 0.075 | 0.064 |
| Engineering | 0.055 | 0.090 | 0.060 |
| FHSS | 0.060 | 0.075 | 0.062 |
| Humanities | 0.015 | 0.038 | 0.018 |
| Life | 0.217 | 0.184 | 0.213 |
| Nursing | 0.051 | 0.033 | 0.049 |
Practice: Age vs. Distracted Driving
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
Of those cell phone distracted drivers, what proportion are 15-19?
- 58/456
Is this a conditional or marginal proportion?
- Conditional
Practice 5.2 Questions 1-2
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
-
Of those drivers aged 40-49, what proportion are not distracted?
-
Is this a conditional or marginal proportion?
Practice 5.2 Questions 1-2 Answers
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
-
Of those drivers aged 40-49, what proportion are not distracted?
- 7328/7797
-
Is this a conditional or marginal proportion?
- Conditional
Practice 5.2 Questions 3-4
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
-
What proportion of drivers are distracted by cell phones?
-
Is this a conditional or marginal proportion?
Practice 5.2 Questions 3-4 Answers
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
-
What proportion of drivers are distracted by cell phones?
- 456/50683
-
Is this a conditional or marginal proportion?
- Marginal
Practice: Age vs. Distracted Driving
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
What is the conditional distribution of age for those who are cell phone distracted?
Practice: Age vs. Distracted Driving
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
What is the conditional distribution of age for those who are cell phone distracted?
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 0.127 | 0.349 | 0.211 | 0.151 | 0.105 | 0.046 | 0.011 | 1 |
Practice: Age vs. Distracted Driving
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
What is the conditional distribution of age for those who are cell phone distracted?
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 0.127 | 0.349 | 0.211 | 0.151 | 0.105 | 0.046 | 0.011 | 1 |
| Not Distracted | 0.063 | 0.240 | 0.178 | 0.156 | 0.159 | 0.112 | 0.092 | 1 |
| Other Distracted | 0.096 | 0.283 | 0.185 | 0.126 | 0.131 | 0.091 | 0.089 | 1 |
| Margin (Overall) | 0.066 | 0.243 | 0.179 | 0.154 | 0.157 | 0.110 | 0.091 | 1 |
Practice: Age vs. Distracted Driving
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
What is the conditional distribution of distracted for those aged 20-29?
Practice: Age vs. Distracted Driving
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
What is the conditional distribution of distracted for those aged 20-29?
| 20-29 | |
|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 0.013 |
| Not Distracted | 0.914 |
| Other Distracted | 0.073 |
| Sum | 1.000 |
Practice: Age vs. Distracted Driving
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
What is the conditional distribution of distracted for those aged 20-29?
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Margin (Overall) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 0.017 | 0.013 | 0.011 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.001 | 0.009 |
| Not Distracted | 0.891 | 0.914 | 0.925 | 0.940 | 0.942 | 0.945 | 0.938 | 0.928 |
| Other Distracted | 0.091 | 0.073 | 0.065 | 0.051 | 0.052 | 0.052 | 0.061 | 0.063 |
Using the Analysis Tool

Using the Analysis Tool

Using the Analysis Tool

Using the Analysis Tool
Of those drivers aged 30-39, what proportion are not distracted?

Using the Analysis Tool
Of those “other distracted” drivers, what proportion are 60-69?

Statistical Model (Population)
The independence population model: The choice of apple vs. android product for a student is independent of the college of the student. In other words, the two variables are independent of each other.
Back to the Phone Example
| Apple | Android | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Business | 557 | 51 | 608 |
| CFAC | 119 | 19 | 138 |
| CMS | 140 | 37 | 177 |
| Education | 95 | 16 | 111 |
| Engineering | 84 | 19 | 103 |
| FHSS | 91 | 16 | 107 |
| Humanities | 23 | 8 | 31 |
| Life | 329 | 39 | 368 |
| Nursing | 77 | 7 | 84 |
| Sum | 1515 | 212 | 1727 |
Consequences of Independent Population Model
Because of independence… \[ \begin{align*} \text{Pr}(\text{Apple & Business}) &= \text{Pr}(\text{Apple})\text{Pr}(\text{Business}) \\ &= (1515/ 1727) \times (608/ 1727) \\ &= 0.309 \end{align*} \]
IF variables are independent, expected number of people in each cell: \[ \begin{align*} \text{Exp. No. of Apple/Business} &= n\times \text{Pr}(\text{Apple})\text{Pr}\times (\text{Business}) \\ &= 1727 \times 0.309 \\ &= 533.364 \end{align*} \]
Independence Model Practice
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
- Under the independence model, what is the probability of being 15-19 and not distracted?
- \((3323/50683)\times (47055/50683) = 0.061\)
Independence Model Practice
| 15-19 | 20-29 | 30-39 | 40-49 | 50-59 | 60-69 | 70+ | Sum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell Phone Distracted | 58 | 159 | 96 | 69 | 48 | 21 | 5 | 456 |
| Not Distracted | 2962 | 11278 | 8382 | 7328 | 7482 | 5282 | 4341 | 47055 |
| Other Distracted | 303 | 898 | 586 | 400 | 415 | 288 | 282 | 3172 |
| Sum | 3323 | 12335 | 9064 | 7797 | 7945 | 5591 | 4628 | 50683 |
- Under the independence model, what is the expected number of 15-19 year old drivers who are not distracted?
- \(0.061 \times 50683 = 3085.132\)
Using the Analysis Tool
Good news! The tool will calculate the expected counts for you. You just need to know where to look…

Hypothesis Testing
Recall the 3 steps of hypothesis testing:
- Formulate hypotheses
- See if data matches (or doesn’t) match the hypotheses
- Draw a conclusions about the parameter
Hypothesis Testing
Research Question: Is there a relationship between which college someone is in and whether they use an apple or android phone?
The hypotheses: \[ \begin{align} H_0: & \text{ College and Phone are Independent}\\ H_a: & \text{ College and Phone are NOT Independent}\\ \end{align} \]
Hypothesis Testing
Step 2: See if the data matches the hypotheses.
How can we compare our observed data to hypotheses?
- Compare our data to what we expect to see IF the variables are independent.
Hypothesis Testing
Step 2: See if the data matches the hypotheses.
How can we compare our observed data to hypotheses?
- Compare our data to what we expect to see IF the variables are independent.
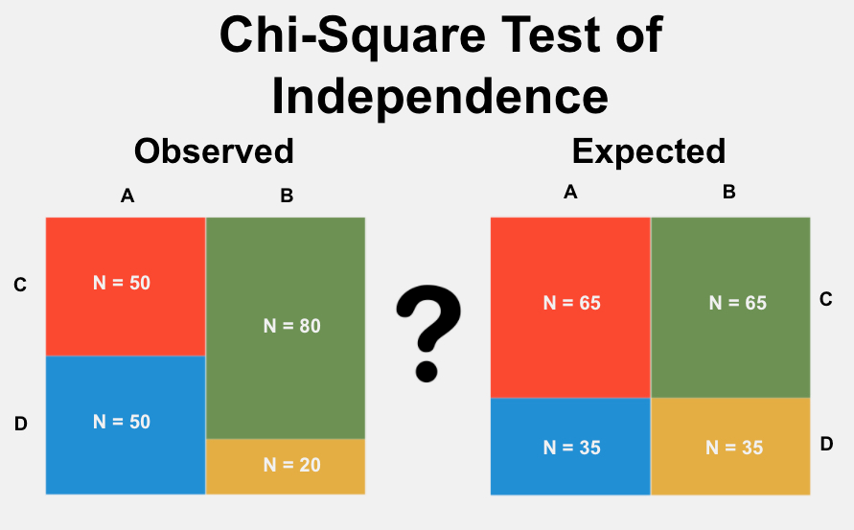
Hypothesis Testing
Step 2: See if the data matches the hypotheses.
How can we compare our observed data to hypotheses?
- Compare our data to what we expect to see IF the variables are independent.
The \(\chi^2\)-statistic: (pronounced “kai-squared”) \[ \begin{align*} \chi^2 &= \sum_{r=1}^R \sum_{c=1}^C \chi^2_{rc} \\ &= \sum_{r=1}^R \sum_{c=1}^C \frac{(\text{Obs}_{rc} - \text{Exp}_{rc})^2}{\text{Exp}_{rc}} \end{align*} \]
Hypothesis Testing
Step 2: See if the data matches the hypotheses. \[ \begin{align*} \chi^2 &= \sum_{r=1}^R \sum_{c=1}^C \frac{(\text{Obs}_{rc} - \text{Exp}_{rc})^2}{\text{Exp}_{rc}} \end{align*} \]
Intuition
- If \(\chi^2\) is big, then the data favor \(H_a\) because what you observed is different than what you expected to observe IF \(H_0\) was true.
- If any individual cell \(\chi^2_{rc}\) is big, then that observed count is very different from what you expected it to be if \(H_0\) were true.
Hypothesis Testing
Step 2: See if the data matches the hypotheses.
If the independence model is appropriate AND all expected counts are \(>\) 5, then the \(\chi^2\) values that you should get when sampling follows an \(\chi^2\)-distribution.

Hypothesis Testing
Step 2: See if the data matches the hypotheses (FIRST - check to make sure all expected counts \(> 5\))
| Apple | Android | |
|---|---|---|
| Business | 533.364 | 74.636 |
| CFAC | 121.060 | 16.940 |
| CMS | 155.272 | 21.728 |
| Education | 97.374 | 13.626 |
| Engineering | 90.356 | 12.644 |
| FHSS | 93.865 | 13.135 |
| Humanities | 27.195 | 3.805 |
| Life | 322.826 | 45.174 |
| Nursing | 73.688 | 10.312 |
Hypothesis Testing

Step 2: See if the data matches the hypotheses.
- \(\chi^2 =\) 33.3255
- \(p\)-value \(=\) 10^{-4}
What is your conclusion at the \(\alpha = 0.05\) level?
- The data are inconsistent with the null hypothesis so we conclude that the college and phone variables are NOT independent.
Using the Analysis Tool
The tool calculates the \(\chi^2_{rc}\) values for you:

Using the Analysis Tool

Practice 5.2 Question 5
Are the conditions met to perform a \(\chi^2\) test for the hypotheses: \[ \begin{align} H_0&: \text{There is NO association between distraction and age} \\ H_A&: \text{There is an association between distraction and age} \end{align} \]
- True
- False
Practice 5.2 Question 5 Answer
Are the conditions met to perform a \(\chi^2\) test for the hypotheses: \[ \begin{align} H_0&: \text{There is NO association between distraction and age} \\ H_A&: \text{There is an association between distraction and age} \end{align} \]
- True - because all expected counts are greater than 5
- False
Practice 5.2 Question 6
What is the conclusion for the test: \[ \begin{align} H_0&: \text{There is NO association between distraction and age} \\ H_A&: \text{There is an association between distraction and age} \end{align} \]
- Reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is an assocation
- Reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is NO assocation
- Fail to reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is an assocation
- Fail to reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is NO assocation
Practice 5.2 Question 6 Answer
What is the conclusion for the test: \[ \begin{align} H_0&: \text{There is NO association between distraction and age} \\ H_A&: \text{There is an association between distraction and age} \end{align} \]
- Reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is an assocation
- Reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is NO assocation
- Fail to reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is an assocation
- Fail to reject \(H_0\) and conclude that there is NO assocation
Following up on \(\chi^2\) Test
IF you reject \(H_0\), what can we say about where the relationship is? In other words, where are observed counts most different from expected counts?
- Check the individual cell \(\chi^2\) values.
Following up on \(\chi^2\) Test
| Apple | Android | |
|---|---|---|
| Business | 1.0 | 7.5 |
| CFAC | 0.0 | 0.3 |
| CMS | 1.5 | 10.7 |
| Education | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| Engineering | 0.4 | 3.2 |
| FHSS | 0.1 | 0.6 |
| Humanities | 0.6 | 4.6 |
| Life | 0.1 | 0.8 |
| Nursing | 0.1 | 1.1 |
| Apple | Android | |
|---|---|---|
| Business | 557 | 51 |
| CFAC | 119 | 19 |
| CMS | 140 | 37 |
| Education | 95 | 16 |
| Engineering | 84 | 19 |
| FHSS | 91 | 16 |
| Humanities | 23 | 8 |
| Life | 329 | 39 |
| Nursing | 77 | 7 |
| Apple | Android | |
|---|---|---|
| Business | 533.4 | 74.6 |
| CFAC | 121.1 | 16.9 |
| CMS | 155.3 | 21.7 |
| Education | 97.4 | 13.6 |
| Engineering | 90.4 | 12.6 |
| FHSS | 93.9 | 13.1 |
| Humanities | 27.2 | 3.8 |
| Life | 322.8 | 45.2 |
| Nursing | 73.7 | 10.3 |
Practice 5.2 Question 7
What is the largest contributor to the relationship between distraction and age in the distracted driving analysis?
- Cell phone distracted, 15-19
- Cell phone distracted, 70+
- Not distracted, 30-39
- Other distracted, 15-19
Practice 5.2 Question 7 Answer
What is the largest contributor to the relationship between distraction and age in the distracted driving analysis?
- Cell phone distracted, 15-19
- Cell phone distracted, 70+
- Not distracted, 30-39
- Other distracted, 15-19
Nuances of \(\chi^2\) Tests
- What do we do if our expected counts aren’t all \(>5\)?
- Go get more data, combined small count categories or ask a statistician.
Key Terminology
- Conditional distributions
- Marginal Distributions
- Side-by-side bar charts
- Chi-square test
- Chi-square statistics