Ethics of Statistical Practice
An Example Study
Do you have any concerns with this experiment?
Ethics in Statistics
Data Science professor at UVA, Rafael Alvarado, asked, “Why are you acquiring data in the first place? What is the business proposition, what is the scientific motivation? What [is the aspect of the] world that you are interested in studying or affecting, that you are acquiring data and doing analysis for? We call that the area of value because that is where the purpose of working with data comes from… where data has an influence on the world, where it can either do good or harm… that is where ethics comes in.”
Dimensions of Ethical Statistics
- Ethical Statistical Practice
- Recognizing and correcting unethical behavior in statistics
Dim 1: Ethical Statistical Practice
American Statistical Association Guidance on Ethical Practice:
- Personal professional integrity and accountability
- Responsibilities to research subjects, data subjects, or those directly affected by statistical practices
- Integrity of data and methods
- Responsibilities to stakeholders
- Responsibilities to members of multidisciplinary teams
- Responsibilities to fellow statistical practitioners and the profession
- Responsibilities of leaders, supervisors, and mentors in statistical practice
- Responsibilities regarding potential misconduct
Dim 1: Ethical Statistical Practice
Personal Integrity & Accountability:-
Take responsibility for your work
- Disclose biases in data
- Disclose how data was collected
- Keep a copy of original data
-
Support decision making with appropriate methodology
- Let data (not personal biases) drive decision making
- Be truthful about your capabilities and activities
Dim 1: Ethical Statistical Practice
Responsibilities to research subjects:
Any study involving human subject must be approved by an Institutional Review Board (IRB) and must adhere to The Belmont Report - a 1978 report outlining ethical guidelines for studies:
- Respect for persons - subjects must be treated as agents and give informed consent.
- Beneficence – weigh potential benefit against potential harm. Benefit must outweigh the risk.
- Justice - equal distribution of burdens and benefits of study. All the risk of negative outcome cannot be given to just one group.
YPoll 1.3 Question 1
Researchers conduct a study where AI creates diet plans for participating subjects, from all age groups. Given the scenario, which of the following is a violation of “respect for persons”?
- Not considering the benefits of an AI created diet relative to the risks
- Collecting sensitive personal information of a subject without their consent
- Giving toddlers strict diets while other age group diets are more appropriate
YPoll 1.3 Question 1 Answer
Researchers conduct a study where AI creates diet plans for participating subjects, from all age groups. Given the scenario, which of the following is an example of “respect for persons”?
- Not considering the benefits of an AI created diet relative to the risks
- Collecting sensitive personal information of a subject without their consent
- Giving toddlers strict diets while other age group diets are more appropriate
Dim 1: Ethical Statistical Practice
Integrity of Data and Methods-
Data Integrity
- Mitigate limitations, defects, or biases in the data
- Data should be representative of whole population (if not then disclose it and state who your results apply to)
-
Method Integrity
- Every method has underlying conditions that should be met (if they are not, proceed with caution and warn of potential impacts)
- Not clearly communicating how the data was analyzed
- Communicate potential impacts on the interpretation, conclusions, recommendations, decisions, or other results of statistical practices.
Data Integrity & Accountability


YPoll 1.3 Question 2
Researchers for the AI diet study quickly realize that the data is biased, but believe nothing could be done to fix this so they proceeded anyway. True or false, this is a violation of “data integrity”?
YPoll 1.3 Question 2 Answer
Researchers for the AI diet study quickly realize that the data is biased, but believe nothing could be done to fix this so they proceeded anyway. True or false, this is a violation of “data integrity”?
- True
Dim 2: Recognizing Ethical Issues
Weapons of Math Destruction
-
3 characteristics to help recognize unethical data behavior:
- Scale
- Opacity (lacking transparency)
- Damage
Dim 2: Recognizing Ethical Issues
Scale
- data and algorithms (a set of rules to make a decision - typically derived from data) being used for a broad class of people
- Issue: removing individuality and making individals part of a “collective”
Opacity
- data & analyses that is not properly documented OR so complex that no one can understand what the decision rules are
- Issue: You can’t evaluate discrimination, justice, fairness, etc.
Damage
- algorithms being used to make “big decisions” (admittance to school, firing, hiring, loans)
- Issue: “big decisions” shouldn’t be solely based on algorithms
YPoll 1.3 Question 3
Scenario: Researchers conduct a study where AI creates diet plans for participating subjects from all age groups. If participants complete their diet successfully, their healthcare premiums decrease by 60%.
Question: The researchers do not understand how the AI creates diet plans or how the AI qualifies a “successful” diet. What principle of unethical use of data does this relate to?
- Scale
- Opacity
- Damage
YPoll 1.3 Question 3 Answer
Scenario: Researchers conduct a study where AI creates diet plans for participating subjects from all age groups. If participants complete their diet successfully, their healthcare premiums decrease by 60%.
Question: The researchers do not understand how the AI creates diet plans or how the AI qualifies a “successful” diet. What principle of unethical use of data does this relate to?
- Scale
- Opacity
- Damage
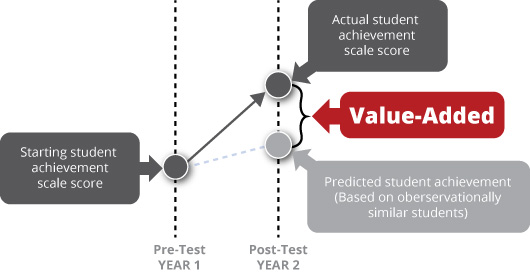
Example: Teacher Evaluations
Analysis Goal: Identify “bad” teachers
Analysis Tool: Value added model
- “statistical processes” developed by professional statisticians use data on a student’s past test scores and demographics to predict the student’s future test scores
- student’s actual score is then compared to the predicted score
- difference between the predicted and actual scores, if any, is assumed to be due to the teacher
Example: Teacher Evaluations
Discussion: How could value added models be unethically used?
- Scale
- Opacity
- Damage
Conclusions
We are NOT saying:
- Don’t use statistical analysis (and algorithms derived from data)
- All uses of data and algorithms are unethical
We ARE saying:
- Be careful in how you use the data you collect
- Evaluate the potential for good (and bad) of your study & analysis
Terminology
- Ethics in statistical practice
- Identifying ethical issues
- Scale
- Opacity
- Damage